Upgrade & Secure Your Future with DevOps, SRE, DevSecOps, MLOps!
We spend hours on Instagram and YouTube and waste money on coffee and fast food, but won’t spend 30 minutes a day learning skills to boost our careers.
Master in DevOps, SRE, DevSecOps & MLOps!
Learn from Guru Rajesh Kumar and double your salary in just one year.
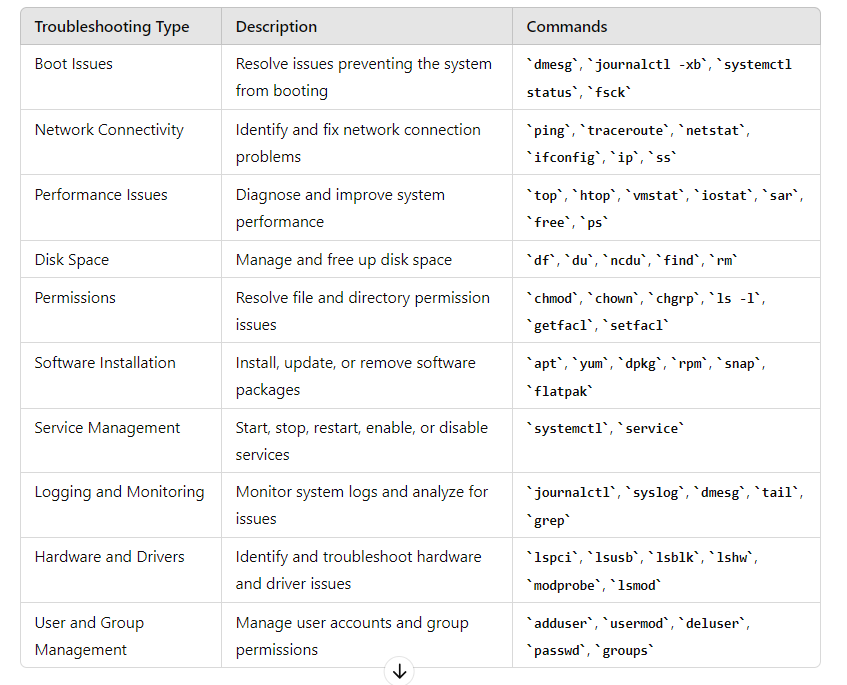
Boot Issues: Check boot logs (dmesg, journalctl -xb), bootloader configuration (grub.cfg).
Networking: Verify network configuration (ifconfig, ip addr), check connectivity (ping, traceroute), review firewall settings (iptables).
Performance: Monitor system resources (top, htop, vmstat), check disk usage (df -h), identify CPU or memory bottlenecks.
Disk Space: Check disk usage (df -h), identify large files/directories (du -sh).
Permissions: Verify file/directory permissions (ls -l, getfacl), ensure correct ownership (chown, chgrp).
Software Installation: Check package installation (dpkg, rpm, apt, yum), verify dependencies.
Service Management: Restart services (systemctl restart <service>), check service status (systemctl status <service>).
Logging and Monitoring: Review system logs (/var/log), use monitoring tools (sar, sysstat, Prometheus, Grafana).
Hardware and Drivers: Check hardware status (lspci, lsusb), verify driver status (lsmod, modprobe).
User and Group Management: Verify user permissions (groups, id), manage user accounts (adduser, usermod, deluser).- dmesg – Displays the kernel ring buffer messages.
- journalctl – Views and manages systemd journal logs.
- ls – Lists directory contents.
- ps – Lists currently running processes.
- top – Displays real-time system information, including CPU and memory usage.
- htop – Interactive process viewer and system monitor.
- df – Shows disk space usage.
- du – Displays disk usage for files and directories.
- free – Shows memory and swap usage.
- uptime – Displays system uptime and load averages.
- netstat – Shows network statistics, connections, and routing tables.
- ifconfig – Displays network interface configuration.
- ip – Shows or manipulates routing, devices, policy routing, and tunnels.
- ping – Sends ICMP Echo Request packets to a network host.
- traceroute – Prints the route packets take to a network host.
- lsof – Lists open files and the processes that opened them.
- ps – Lists information about processes.
- kill – Sends a signal to terminate processes.
- systemctl – Controls systemd services (e.g., start, stop, enable, disable).
- grep – Searches for patterns in files or input.
- tail – Outputs the last part of files.
- cat – Concatenates and displays files.
- less – Displays text files with pagination.
- find – Searches for files and directories.
- cp – Copies files and directories.
- mv – Moves or renames files and directories.
- rm – Removes files and directories.
- chmod – Changes file permissions.
- chown – Changes file owner and group.
- ssh – Securely connects to a remote server.

 Starting: 1st of Every Month
Starting: 1st of Every Month  +91 8409492687 |
+91 8409492687 |  Contact@DevOpsSchool.com
Contact@DevOpsSchool.com
[…] https://www.bestdevops.com/how-to-troubleshoot-in-linux […]