Upgrade & Secure Your Future with DevOps, SRE, DevSecOps, MLOps!
We spend hours on Instagram and YouTube and waste money on coffee and fast food, but won’t spend 30 minutes a day learning skills to boost our careers.
Master in DevOps, SRE, DevSecOps & MLOps!
Learn from Guru Rajesh Kumar and double your salary in just one year.
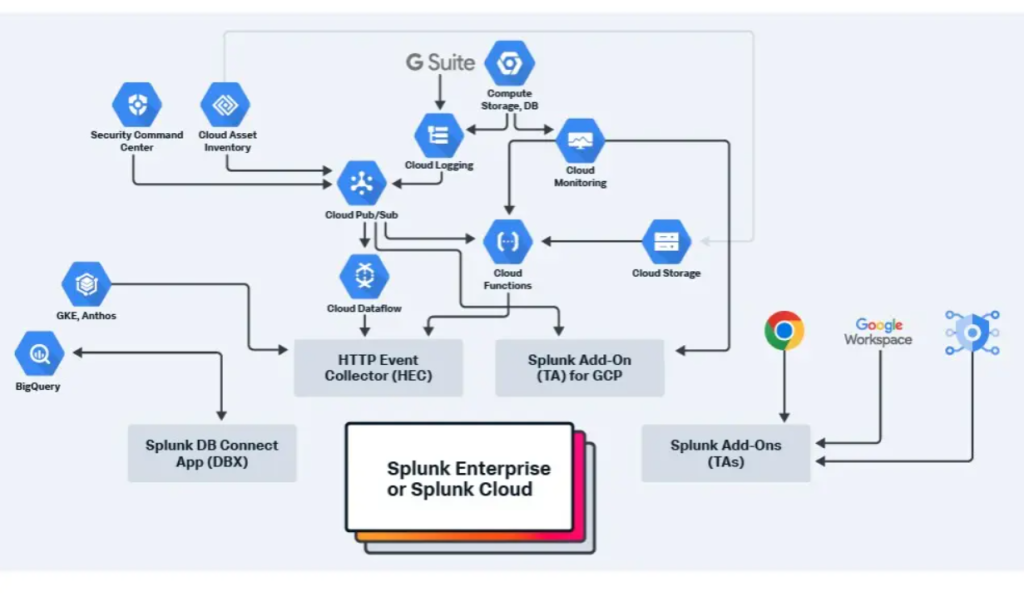
In the fast-evolving world of cloud infrastructure, monitoring, and observability are essential components of a successful DevOps strategy. Google Cloud offers a robust set of tools that empower organizations to monitor and maintain the health of their applications and infrastructure. Through a combination of cloud-native services and DevOps principles, Google Cloud ensures seamless observability and real-time monitoring for applications, enabling teams to make informed decisions and drive continuous improvement.
With a strong focus on scalability, automation, and deep insights, Google Cloud’s DevOps monitoring and observability tools allow teams to proactively address issues, optimize performance, and improve the overall reliability of their systems. This post explores how Google Cloud utilizes DevOps practices to enhance monitoring and observability, as well as the major features that make it a leader in this space.
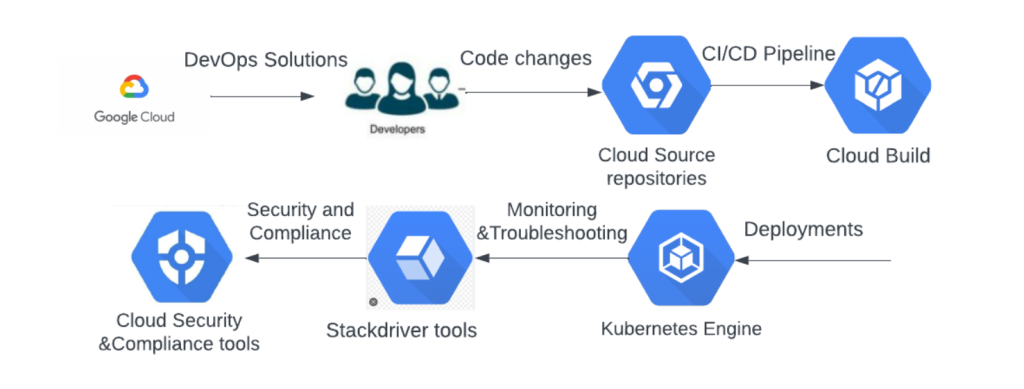
How Google Cloud Implements DevOps in Monitoring
Google Cloud brings together several powerful tools and services to integrate monitoring and observability seamlessly into the DevOps pipeline. These tools help DevOps teams gain deep insights into their systems’ behavior, performance, and overall health.
Key Elements of Google Cloud’s DevOps Monitoring:
- Unified Monitoring Solution: Google Cloud combines monitoring and logging into a single platform, allowing teams to monitor infrastructure, applications, and services from a central location. This centralized approach ensures visibility across all components of the environment.
- Google Cloud Operations Suite (formerly Stackdriver): The Google Cloud Operations Suite is the cornerstone of monitoring in Google Cloud. This suite includes tools like Cloud Monitoring, Cloud Logging, and Cloud Trace, which provide end-to-end visibility into system performance and behavior.
- Integration with CI/CD: Google Cloud tools integrate seamlessly with CI/CD pipelines, providing real-time monitoring throughout the entire software development lifecycle. This integration ensures that monitoring and observability are continuously embedded into the development and deployment process.
- Support for Hybrid and Multi-Cloud Environments: Google Cloud’s monitoring tools are designed to work across hybrid and multi-cloud environments. This flexibility ensures that teams can monitor both on-premises and cloud resources, providing a comprehensive view of system health and performance.
Major Features of Google Cloud’s Monitoring and Observability
Google Cloud offers several innovative features that stand out in the realm of monitoring and observability. These features are built to optimize system performance, detect anomalies, and help DevOps teams proactively manage their infrastructure.
Key Features of Google Cloud’s Monitoring Tools:
- Real-Time Monitoring and Alerts: Google Cloud’s tools provide real-time monitoring, ensuring that teams can track system performance as it happens. Customizable alerts can notify teams of any issues, such as downtime, latency, or resource exhaustion, allowing for fast remediation.
- Comprehensive Logging: Cloud Logging collects, stores, and analyzes logs from applications, systems, and services, enabling DevOps teams to detect issues and investigate root causes. Logs are indexed and searchable, making it easy to find specific events that might indicate performance problems.
- Distributed Tracing and Cloud Trace: Google Cloud includes distributed tracing tools that allow teams to track requests across services. Cloud Trace enables teams to visualize latency and pinpoint bottlenecks in a microservices architecture, which is vital for optimizing application performance.
- Cloud Profiler: Cloud Profiler allows developers to continuously analyze the performance of applications in production. By identifying CPU and memory bottlenecks, Cloud Profiler helps optimize application code, ensuring better performance and resource utilization.
- Scalability and Flexibility: Google Cloud’s monitoring tools are designed to scale with the growing needs of organizations. Whether you are running a small app or managing a global enterprise infrastructure, the platform is built to handle large datasets and complex environments.
How Google Cloud Helps with Proactive Issue Detection
Google Cloud’s monitoring tools don’t just provide visibility; they also help teams proactively detect and address issues before they escalate into critical problems. By leveraging machine learning, automation, and real-time monitoring, Google Cloud enables faster identification of anomalies and potential issues.
Features for Proactive Issue Detection:
- Anomaly Detection with Machine Learning: Google Cloud utilizes machine learning models to automatically detect anomalies in application performance, resource usage, and network traffic. These models learn the normal behavior of systems and can flag irregularities, helping DevOps teams detect issues early.
- Automated Alerts and Incident Management: Customizable alerting mechanisms in Google Cloud enable automated responses to performance issues. For example, an alert might trigger a remediation action or escalate the issue to the appropriate team, reducing manual intervention.
- Root Cause Analysis with Logs and Traces: When issues arise, Google Cloud’s integrated tools enable DevOps teams to quickly perform root cause analysis. By combining logs, metrics, and traces, teams can identify exactly where and why a problem occurred.
- Health Checks and Service Level Objectives (SLOs): Google Cloud’s monitoring suite helps teams define service-level objectives (SLOs) and track whether they are being met. Health checks are integrated into this process, providing continuous feedback on the performance and availability of services.
Benefits of Using Google Cloud for DevOps Monitoring and Observability
Google Cloud’s monitoring and observability tools offer numerous benefits to DevOps teams, helping them improve the performance, reliability, and security of their applications.
Key Benefits Include:
- Faster Issue Resolution: With real-time insights, alerts, and a unified monitoring platform, DevOps teams can respond to issues faster. The ability to identify problems early in the lifecycle ensures that teams can fix them before they impact users.
- Increased System Reliability: Google Cloud’s monitoring tools enable proactive management of infrastructure, reducing downtime and increasing the overall reliability of systems. This leads to a better user experience and a higher level of customer satisfaction.
- Cost Optimization: By providing detailed insights into resource utilization and performance, Google Cloud helps teams optimize their infrastructure. Teams can identify underutilized resources and scale them back, reducing unnecessary costs.
- Collaboration Across Teams: Google Cloud’s tools provide a collaborative platform where developers, operations teams, and other stakeholders can share insights, logs, and dashboards. This fosters collaboration and drives quicker decision-making.
- Seamless Integration with Google Cloud Services: As a native Google Cloud solution, the monitoring tools integrate seamlessly with other Google Cloud services. This tight integration ensures that monitoring is aligned with the rest of the infrastructure, providing a cohesive and optimized experience.
Continuous Improvement with Google Cloud’s DevOps Monitoring
Google Cloud’s monitoring and observability tools are not just about tracking performance; they are about fostering continuous improvement. By using data-driven insights, DevOps teams can continuously refine and enhance their applications and systems.
How Google Cloud Facilitates Continuous Improvement:
- Continuous Feedback Loops: By integrating monitoring into every stage of the development lifecycle, Google Cloud ensures that teams receive constant feedback on system performance. This ongoing loop allows teams to make iterative improvements based on real-world data.
- Optimization of Development and Deployment Pipelines: Google Cloud’s monitoring tools are tightly integrated with DevOps workflows. This integration ensures that teams can continuously monitor their applications as they are developed and deployed, ensuring that new releases don’t degrade performance or introduce new issues.
- Improved Quality and Testing: By monitoring performance during testing phases, Google Cloud helps teams identify issues early in the development cycle. This leads to higher-quality applications and reduced bugs during production.
- Scaling with Confidence: Google Cloud’s tools allow teams to scale their applications and infrastructure with confidence. With full visibility into system performance, teams can make data-driven decisions when scaling their environment to meet growing demands.
Google Cloud’s Impact on DevOps Monitoring and Observability
Google Cloud’s suite of monitoring and observability tools offers a comprehensive, scalable, and integrated solution for DevOps teams looking to ensure system performance, reliability, and security. By leveraging real-time monitoring, automated issue detection, and AI-driven insights, Google Cloud empowers organizations to continuously optimize their infrastructure and applications.
With a focus on scalability, cost optimization, and deep insights into application behavior, Google Cloud’s monitoring solutions play a critical role in helping DevOps teams streamline their workflows, improve system performance, and maintain high availability. Whether you are managing a global infrastructure or building new cloud-native applications, Google Cloud provides the tools needed to monitor and maintain peak performance across all environments.

 Starting: 1st of Every Month
Starting: 1st of Every Month  +91 8409492687 |
+91 8409492687 |  Contact@DevOpsSchool.com
Contact@DevOpsSchool.com