Upgrade & Secure Your Future with DevOps, SRE, DevSecOps, MLOps!
We spend hours on Instagram and YouTube and waste money on coffee and fast food, but won’t spend 30 minutes a day learning skills to boost our careers.
Master in DevOps, SRE, DevSecOps & MLOps!
Learn from Guru Rajesh Kumar and double your salary in just one year.
Kubernetes is an open-source container orchestration platform that automates the deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications. In the context of DevOps, Kubernetes plays a crucial role in enabling continuous integration, continuous delivery, and infrastructure management. By managing containers across multiple environments, Kubernetes ensures that applications are scalable, resilient, and easily maintainable—key aspects of any DevOps workflow.
This post explores how to implement DevOps practices using Kubernetes, highlighting the major features that make Kubernetes an ideal platform for automating DevOps processes and streamlining the development lifecycle.
Setting Up Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery (CI/CD) with Kubernetes
One of the primary goals of DevOps is to establish a smooth and automated flow for software delivery. Kubernetes facilitates this by integrating with CI/CD pipelines, allowing for automated deployment, testing, and scaling of applications in various environments.
How Kubernetes Facilitates CI/CD:
- Automated Deployments: Kubernetes simplifies the deployment process by using declarative configurations (e.g., YAML files) to define the desired state of applications. Continuous integration tools like Jenkins, GitLab CI, or CircleCI can be integrated with Kubernetes to automate the deployment process.
- Scaling Applications: Kubernetes automatically scales applications based on traffic, resource utilization, or custom metrics. This allows DevOps teams to implement auto-scaling policies in their CI/CD pipelines to optimize resource usage.
- Rollbacks and Version Control: Kubernetes supports seamless rollbacks to previous versions of an application, which is essential for maintaining stability during continuous delivery. It helps teams quickly revert to a stable state in case of deployment failures.
- Blue-Green and Canary Deployments: Kubernetes supports deployment strategies like blue-green and canary deployments, where new versions of applications are tested in production with minimal risk. This allows DevOps teams to reduce downtime and improve the reliability of software releases.
- Integration with GitOps: Kubernetes works well with GitOps practices, where the desired state of the application is defined in Git repositories. Changes to the application are automatically deployed by Kubernetes, providing a seamless and automated flow from development to production.
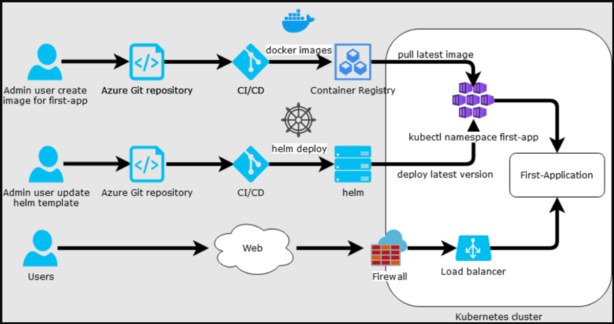
Infrastructure as Code (IaC) with Kubernetes
Infrastructure as Code (IaC) is a key DevOps practice that enables teams to manage and provision infrastructure using code, ensuring consistency and scalability. Kubernetes plays a vital role in IaC by allowing DevOps teams to define infrastructure and application configurations in code, making it easy to automate deployments and manage environments.
Implementing IaC with Kubernetes:
- Declarative Configuration: Kubernetes uses YAML or JSON files to define application resources like pods, services, and deployments. These files act as declarative configurations, specifying the desired state of the application, which Kubernetes automatically enforces.
- Version Control for Infrastructure: By storing Kubernetes configuration files in Git repositories, DevOps teams can manage infrastructure changes in the same way as application code. This ensures traceability, versioning, and collaboration on infrastructure management.
- Automating Provisioning: Tools like Helm, Kustomize, and Terraform can be used alongside Kubernetes to automate the provisioning of cloud resources, such as virtual machines, storage, and networking, in addition to managing Kubernetes clusters.
- Consistent Environments: Kubernetes ensures that the application environment remains consistent across different stages of development, testing, and production. This eliminates the “works on my machine” problem, making it easier to move applications through the pipeline.
- Immutable Infrastructure: Kubernetes promotes the use of immutable infrastructure, where changes are made by replacing entire containers or services rather than modifying existing ones. This enhances system stability and reduces configuration drift.
Automating Application Management with Kubernetes
Kubernetes simplifies the management of applications by automating key processes such as scaling, monitoring, and recovery. This automation reduces the operational burden on DevOps teams and ensures that applications are resilient and responsive to changing workloads.
Key Automation Features of Kubernetes:
- Auto-Scaling: Kubernetes automatically adjusts the number of running instances of an application based on real-time metrics like CPU usage or traffic. This ensures that applications are always available and responsive to user demands.
- Self-Healing: Kubernetes provides self-healing capabilities by automatically replacing failed containers or nodes. If an application pod crashes, Kubernetes will automatically restart it, ensuring high availability without manual intervention.
- Rolling Updates: Kubernetes allows for rolling updates, where new versions of applications are deployed incrementally. This minimizes downtime and ensures that users are always served by a working version of the application.
- Resource Management: Kubernetes helps optimize resource usage by assigning CPU and memory limits to application containers. It ensures that each application gets the necessary resources without over-consuming or under-utilizing the available infrastructure.
- Service Discovery and Load Balancing: Kubernetes automatically manages service discovery and load balancing, ensuring that traffic is routed to healthy instances of an application. This eliminates the need for manual configuration and improves system reliability.
Monitoring and Observability with Kubernetes in DevOps
Monitoring is a critical aspect of any DevOps process, ensuring that teams can identify and address issues in real time. Kubernetes offers various features that integrate with monitoring and observability tools to provide deep insights into application health and performance.
Monitoring and Observability Features of Kubernetes:
- Integrated Logging: Kubernetes integrates with logging tools like Fluentd, Elasticsearch, and Kibana (EFK stack) to collect and analyze logs from containers, pods, and nodes. This helps teams gain insights into application behavior and troubleshoot issues.
- Prometheus and Grafana Integration: Kubernetes works seamlessly with Prometheus for monitoring system metrics, such as CPU usage, memory usage, and network traffic. These metrics can be visualized in Grafana dashboards, allowing DevOps teams to monitor application performance in real time.
- Health Checks: Kubernetes provides built-in health checks, such as liveness and readiness probes, to monitor the health of containers and applications. If an application fails a health check, Kubernetes automatically restarts or replaces the container.
- Centralized Monitoring: Kubernetes allows for centralized monitoring, where multiple clusters and services are monitored from a single platform. This enables DevOps teams to track the performance and health of the entire system from a unified dashboard.
- Alerting and Notifications: Kubernetes integrates with alerting tools like Alertmanager to notify teams when certain thresholds are crossed, such as high memory usage or application downtime. This ensures that teams can respond quickly to critical incidents.
Enhancing Security in DevOps with Kubernetes
Security is a critical concern in any DevOps process, and Kubernetes offers several features to help teams secure their applications, infrastructure, and workflows. Kubernetes integrates with security tools and practices to ensure that DevOps teams can build and deploy secure software.
Security Features of Kubernetes in DevOps:
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Kubernetes provides RBAC to manage access to cluster resources. By defining roles and permissions, teams can control who has access to specific parts of the infrastructure and limit the risk of unauthorized access.
- Pod Security Policies: Kubernetes allows teams to define security policies that specify how containers should be configured. These policies help ensure that containers run in a secure environment with the right privileges and resources.
- Secrets Management: Kubernetes integrates with tools like HashiCorp Vault to securely manage secrets, such as API keys, passwords, and certificates. Secrets are stored encrypted and can be accessed by applications without exposing sensitive information.
- Network Policies: Kubernetes supports network policies that define how pods communicate with each other. These policies can restrict traffic between pods, reducing the attack surface and improving application security.
- Image Scanning: Kubernetes can integrate with image scanning tools like Clair or Anchore to scan container images for vulnerabilities before they are deployed. This ensures that only secure images are used in production environments.
Kubernetes and DevOps Automation
Kubernetes plays a central role in automating many aspects of the DevOps lifecycle, from continuous integration and delivery to infrastructure management, monitoring, and security. By using Kubernetes to automate tasks, DevOps teams can streamline workflows, increase efficiency, and improve the overall quality and stability of applications.
With Kubernetes, teams can deploy and manage applications more consistently, scale them efficiently, and maintain high availability with minimal manual intervention. Whether you’re managing cloud-native applications, microservices, or hybrid environments, Kubernetes provides the automation and flexibility needed to support modern DevOps practices.

 Starting: 1st of Every Month
Starting: 1st of Every Month  +91 8409492687 |
+91 8409492687 |  Contact@DevOpsSchool.com
Contact@DevOpsSchool.com