Upgrade & Secure Your Future with DevOps, SRE, DevSecOps, MLOps!
We spend hours on Instagram and YouTube and waste money on coffee and fast food, but won’t spend 30 minutes a day learning skills to boost our careers.
Master in DevOps, SRE, DevSecOps & MLOps!
Learn from Guru Rajesh Kumar and double your salary in just one year.
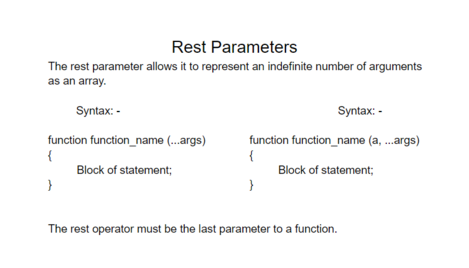
The rest parameter syntax allows a function to accept an indefinite number of arguments as an array, providing a way to represent variadic functions in JavaScript.
Now, What is variadic function ?
In mathematics and in computer programming, a variadic function is a function of indefinite arity, i.e., one which accepts a variable number of arguments. Support for variadic functions differs widely among programming languages.
What is Rest parameter
A function definition’s last parameter can be prefixed with “...” , which will cause all remaining (user supplied) parameters to be placed within a “standard” JavaScript array.. Only the last parameter in a function definition can be a rest parameter.
JavaScript Demo: Functions Rest Parameters
| function sum(...theArgs) { | |
| return theArgs.reduce((previous, current) => { | |
| return previous + current; | |
| }); | |
| } | |
| console.log(sum(1, 2, 3)); | |
| // expected output: 6 | |
| console.log(sum(1, 2, 3, 4)); | |
| // expected output: 10 | |
| // -------------------------------------------------------------------- | |
| function myFun(a, b, ...manyMoreArgs) { | |
| console.log("a", a) | |
| console.log("b", b) | |
| console.log("manyMoreArgs", manyMoreArgs) | |
| } | |
| myFun("one", "two", "three", "four", "five", "six") | |
| // Console Output: | |
| // a, one | |
| // b, two | |
| // manyMoreArgs, ["three", "four", "five", "six"] | |
| // -------------------------------------------------------------------- | |
| const mSum = (num1, num2, ...args)=>{ | |
| console.log(num1); | |
| console.log(num2); | |
| console.log(args); | |
| let sum = num1 + num2; | |
| for(let i=0; i<args.length; i++){ | |
| sum += args[i] | |
| } | |
| } | |
| mSum (1,2,3,4,5,6); | |
| // ------------------------------------------------------------------------ |
