Upgrade & Secure Your Future with DevOps, SRE, DevSecOps, MLOps!
We spend hours on Instagram and YouTube and waste money on coffee and fast food, but won’t spend 30 minutes a day learning skills to boost our careers.
Master in DevOps, SRE, DevSecOps & MLOps!
Learn from Guru Rajesh Kumar and double your salary in just one year.
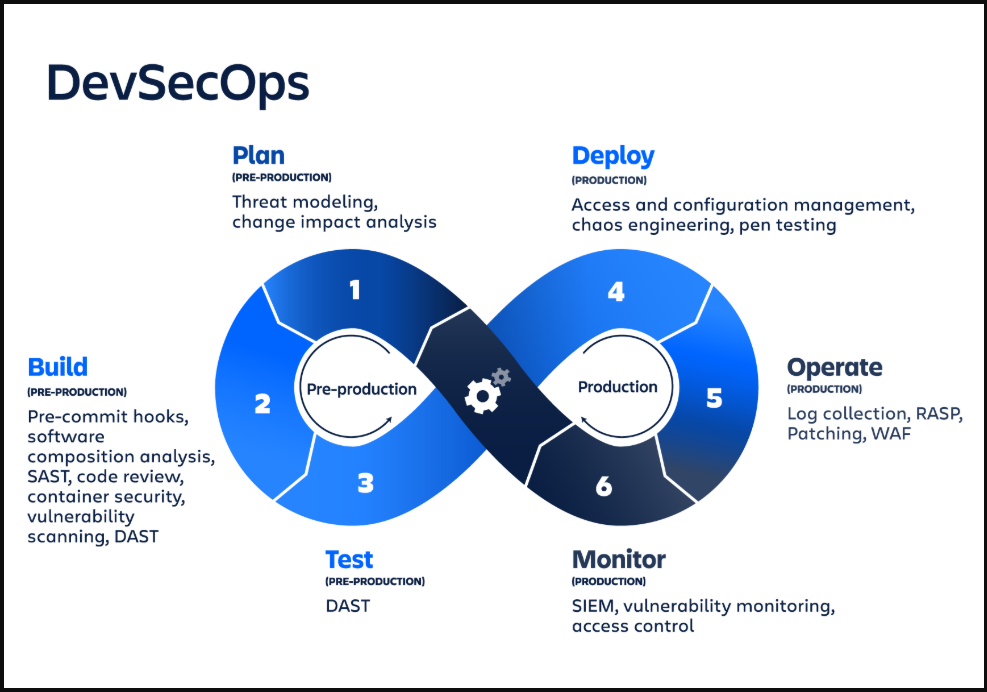
DevOps is a set of practices that aims to unify software development (Dev) and IT operations (Ops). By emphasizing automation, collaboration, and continuous improvement, DevOps ensures that software is delivered faster, more reliably, and with higher quality. DevOps is often structured into four key stages, each playing a vital role in optimizing the software development lifecycle.
These four stages—Plan, Develop, Build, and Monitor—represent the continuous process of software delivery. By understanding and optimizing these stages, organizations can streamline their development processes and deliver better products to their customers. This post will explore each of these stages in detail, highlighting their major features and importance in the DevOps pipeline.
1. Plan
Major Features:
- Defining Requirements and Roadmap:
- The Plan stage is the foundation of the DevOps pipeline. It involves understanding business requirements, defining clear objectives, and setting a roadmap for the development process.
- In this stage, teams collaborate to identify features, fixes, and improvements needed for the software product. Stakeholders, including product managers and developers, ensure that everyone aligns on project goals.
- Agile Planning and Iterations:
- Agile methodologies are often employed during this stage to facilitate iterative development and flexibility. Teams work in short cycles (sprints), enabling continuous delivery of value while adapting to changing requirements.
- Tools like Jira and Trello are often used to manage tasks, track progress, and ensure that the development process stays on track.
- Risk Assessment and Resource Allocation:
- During the planning stage, risks are identified, and mitigation strategies are developed. Resource allocation is also considered, including determining team roles, hardware, and software resources required for the project.
- A successful plan ensures that the DevOps pipeline runs smoothly throughout its life cycle, avoiding delays and miscommunication.
- Collaborative Goal Setting:
- The Plan stage encourages collaboration across all teams, including development, operations, and business units, ensuring that everyone is working toward a shared vision.
2. Develop
Major Features:
- Code Development and Feature Implementation:
- The Develop stage involves writing the code and implementing features defined during the planning phase. Developers work to build and integrate functionalities that meet the business requirements outlined in the Plan.
- At this stage, developers collaborate closely with other team members, ensuring that the code is both functional and maintainable.
- Version Control and Collaboration:
- Version control tools like Git and GitHub are essential in the development stage to ensure that code changes are tracked, merged, and reviewed efficiently.
- Collaboration tools help developers work together in real-time, regardless of their physical locations, to solve problems and speed up development.
- Code Reviews and Quality Assurance:
- Continuous code reviews are conducted to ensure that best practices are followed, reducing bugs and improving overall code quality.
- Automated testing frameworks like JUnit or Selenium can be integrated into the development process to continuously validate code as it’s written.
- Integration with CI/CD:
- As part of the DevOps cycle, the Develop stage is closely tied to Continuous Integration (CI). Developers frequently integrate their code changes into a shared repository to detect issues early in the development process.
- CI tools like Jenkins help automate the process of running unit tests, ensuring that new code does not break existing functionality.
3. Build
Major Features:
- Automated Build Processes:
- The Build stage is responsible for compiling and packaging the code into executable units. This step ensures that the code is ready for deployment and integrates all parts of the application into a single build artifact.
- Automation tools like Maven, Gradle, and Docker ensure that the build process is streamlined, repeatable, and free of errors.
- Continuous Integration and Delivery:
- In DevOps, the Build stage is critical for continuous integration and delivery (CI/CD). As soon as code is written and committed, the CI/CD pipeline automates the process of building the application, running tests, and deploying it to various environments.
- This stage ensures that software is consistently and reliably delivered to production, with minimal manual intervention.
- Unit and Integration Testing:
- Automated testing plays a crucial role in the Build stage. Unit tests, integration tests, and static code analysis are often performed to ensure that the application is functioning as expected and that no new issues are introduced.
- Tools like JUnit, SonarQube, and Mockito are used to verify the quality of the code during the Build phase.
- Dependency Management:
- Managing dependencies (libraries, frameworks, and services) is a key part of the Build process. Tools like Nexus or Artifactory help ensure that all dependencies are tracked, updated, and packaged correctly, making the build process more efficient.
4. Monitor
Major Features:
- Real-Time Monitoring and Logging:
- The Monitor stage involves continuously monitoring the application and infrastructure to ensure optimal performance. Real-time monitoring allows teams to identify bottlenecks, errors, and potential issues before they impact users.
- Tools like Prometheus, Grafana, and New Relic are used to track system performance, user interactions, and application health.
- Incident Management and Response:
- The Monitor stage is critical for incident management. Tools like PagerDuty and Opsgenie help teams respond quickly to outages or performance degradation by alerting the relevant stakeholders.
- Automated workflows are set up to ensure that incidents are addressed swiftly and that teams can investigate root causes effectively.
- Feedback Loops and Continuous Improvement:
- Feedback loops are established to continuously improve the development and operational processes. Data collected during monitoring is analyzed to identify trends, improve software performance, and refine the DevOps pipeline.
- Teams use this feedback to adjust future releases, enhance user experience, and improve overall system reliability.
- Security Monitoring:
- In modern DevOps practices, security is integrated into every stage of the pipeline, including monitoring. Tools like OWASP ZAP and Snyk are used to detect vulnerabilities and prevent security breaches in production.
- Continuous security monitoring helps safeguard the application and data from emerging threats.
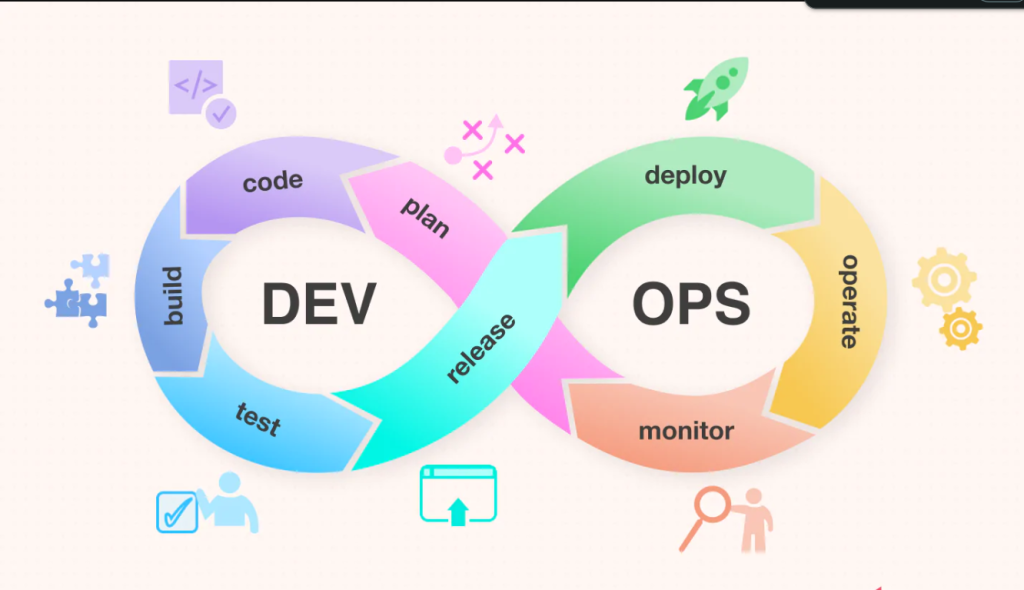
The Continuous DevOps Cycle
The four key stages of DevOps—Plan, Develop, Build, and Monitor—create a continuous cycle of development, integration, and feedback that optimizes the software delivery process. These stages are interconnected, with each one building upon the last to ensure that software is released quickly, reliably, and securely.
By focusing on collaboration, automation, and continuous improvement, DevOps allows organizations to meet the growing demands of their customers, deliver high-quality products faster, and maintain a competitive edge in the market.

 Starting: 1st of Every Month
Starting: 1st of Every Month  +91 8409492687 |
+91 8409492687 |  Contact@DevOpsSchool.com
Contact@DevOpsSchool.com