Upgrade & Secure Your Future with DevOps, SRE, DevSecOps, MLOps!
We spend hours on Instagram and YouTube and waste money on coffee and fast food, but won’t spend 30 minutes a day learning skills to boost our careers.
Master in DevOps, SRE, DevSecOps & MLOps!
Learn from Guru Rajesh Kumar and double your salary in just one year.
DevOps is a set of practices and cultural philosophies that aims to unify software development (Dev) and IT operations (Ops). By fostering collaboration, automating manual processes, and encouraging continuous improvement, DevOps helps organizations deliver high-quality software at faster speeds. The core features of DevOps are designed to streamline the entire software development lifecycle (SDLC) and enhance the efficiency of both development and operations teams.
In this post, we will explore the key features of DevOps, emphasizing how each one contributes to successful software delivery and operational excellence.
1. Collaboration and Communication
Major Features:
- Breaking Down Silos:
- DevOps emphasizes collaboration between development, operations, and quality assurance (QA) teams. By breaking down traditional silos, teams can work together more effectively, resulting in faster and more efficient software delivery.
- Cross-Functional Teams:
- DevOps promotes the creation of cross-functional teams where developers, operations staff, and other stakeholders (such as business analysts) work together throughout the software lifecycle. This fosters shared responsibility for the end product and encourages continuous feedback.
- Increased Transparency:
- Transparent communication across teams ensures that everyone is aligned and aware of progress, challenges, and goals. Tools like Slack, Jira, and Trello facilitate open communication and issue tracking.
- Faster Decision-Making:
- With enhanced collaboration, teams can make decisions quickly, enabling rapid response to changes in requirements, bug fixes, or any other challenges.
2. Automation
Major Features:
- Automating Repetitive Tasks:
- One of the key principles of DevOps is automation. Repetitive tasks like testing, integration, deployment, and infrastructure management can be automated using tools like Jenkins, Ansible, and Terraform.
- Continuous Integration and Delivery (CI/CD):
- Automation is heavily utilized in CI/CD pipelines, which automatically build, test, and deploy software. CI/CD practices enable faster releases with less manual intervention, reducing human error and speeding up time to market.
- Automated Testing:
- Testing is an essential part of DevOps. Automated tests, such as unit tests, integration tests, and acceptance tests, ensure that new changes do not break existing functionality and that the software meets quality standards before deployment.
- Infrastructure as Code (IaC):
- IaC allows teams to automate the provisioning and management of infrastructure, ensuring that environments are consistent, scalable, and easy to reproduce across different stages (development, testing, production).
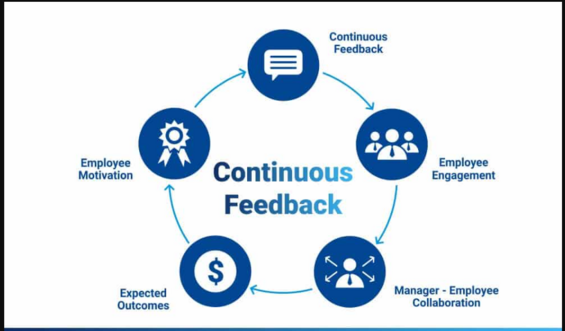
3. Continuous Monitoring and Feedback
Major Features:
- Real-Time System Monitoring:
- Continuous monitoring ensures that systems are actively observed to detect any issues that may arise. Tools like Prometheus, Grafana, and Nagios provide real-time data on the health and performance of applications and infrastructure.
- Feedback Loops:
- DevOps emphasizes the importance of feedback loops. Continuous feedback from monitoring systems, end-users, and automated tests helps teams identify bottlenecks, system performance issues, and areas for improvement.
- Incident Management:
- Automated alerts and incident management tools like PagerDuty and Opsgenie enable teams to respond to issues quickly, minimizing downtime and improving service reliability.
- Data-Driven Decision Making:
- Monitoring tools collect valuable data that helps teams make informed decisions. Continuous feedback from these systems ensures that any necessary adjustments are made to improve performance, stability, and security.
4. Security Integration (DevSecOps)
Major Features:
- Security as Part of the Development Process:
- DevOps encourages the integration of security practices into every stage of the software lifecycle. This approach, known as DevSecOps, ensures that security vulnerabilities are identified and addressed early in the development process rather than after deployment.
- Automated Security Testing:
- Automated security testing tools like OWASP ZAP and Snyk scan code for vulnerabilities and ensure that security policies are continuously enforced. This reduces the chances of security breaches and enhances the overall security posture of applications.
- Continuous Compliance:
- Compliance with regulatory standards (such as GDPR or HIPAA) is maintained through automated checks and audits, ensuring that security requirements are consistently met across the SDLC.
- Risk Management:
- DevOps integrates proactive risk management strategies. Continuous scanning for vulnerabilities, patch management, and automated updates ensure that potential risks are mitigated before they impact production.
5. Scalability and Flexibility
Major Features:
- Elastic Scaling:
- DevOps practices make it easier to scale applications and infrastructure according to demand. Cloud platforms like AWS, Google Cloud, and Azure provide on-demand resources, allowing organizations to scale up or down based on usage patterns.
- Microservices Architecture:
- DevOps supports the use of microservices, where applications are broken down into smaller, independently deployable services. This modular approach allows individual components to scale independently, optimizing resource usage and reducing bottlenecks.
- Containerization:
- Container technologies like Docker and container orchestration platforms like Kubernetes enable teams to deploy applications in lightweight, portable containers that can run consistently across any environment, ensuring flexibility and scalability.
- Elastic Load Balancing:
- With automated load balancing, DevOps ensures that resources are allocated dynamically to handle varying levels of traffic, improving the scalability and availability of applications.
6. Faster Recovery and High Availability
Major Features:
- Automated Rollback:
- DevOps provides the ability to automatically roll back failed deployments. This ensures that any issues are quickly rectified, and downtime is minimized.
- Resilient System Design:
- By implementing principles such as redundancy and failover within the system architecture, DevOps ensures high availability and reliability even in the event of a failure. Automated testing and continuous monitoring help teams detect and fix issues early before they affect end-users.
- Self-Healing Systems:
- DevOps includes features for automated recovery, such as automatically restarting a failed service or container. This reduces the need for manual intervention and ensures that the system remains operational, minimizing downtime.
- Incident Response:
- With continuous monitoring and automated alerting, DevOps teams can respond to system failures in real time, reducing the time it takes to resolve issues and ensuring the availability of services.
The Comprehensive Features of DevOps
DevOps features combine automation, collaboration, continuous feedback, and security integration to enable faster, more reliable software delivery. By adopting these features, organizations can significantly improve their ability to release high-quality software quickly and efficiently, while ensuring scalability, security, and high availability.
These features allow teams to automate key processes, increase collaboration, and continuously improve systems and applications. As businesses strive for greater agility, DevOps provides the foundation for a sustainable and effective software delivery pipeline.