Upgrade & Secure Your Future with DevOps, SRE, DevSecOps, MLOps!
We spend hours on Instagram and YouTube and waste money on coffee and fast food, but won’t spend 30 minutes a day learning skills to boost our careers.
Master in DevOps, SRE, DevSecOps & MLOps!
Learn from Guru Rajesh Kumar and double your salary in just one year.
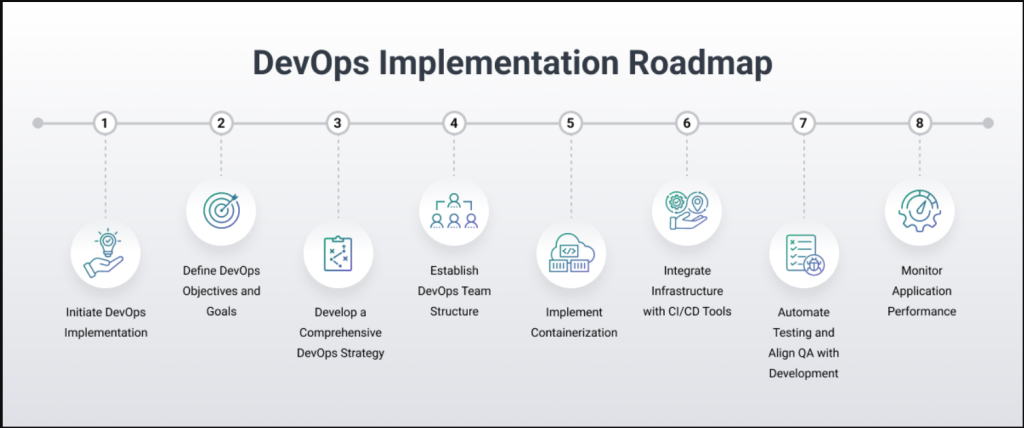
DevOps implementation strategies are crucial for organizations looking to integrate development and operations teams effectively. By adopting the right DevOps strategy, businesses can streamline their software delivery processes, improve collaboration, and enhance the overall efficiency of their IT operations. A well-structured strategy not only aligns teams but also ensures continuous improvement and scalability.
DevOps implementation is not one-size-fits-all; it varies based on organizational needs, the complexity of systems, and the maturity of existing processes. This post will explore the core strategies for implementing DevOps, highlighting their major features, and offering practical insights into making DevOps work for your organization.
1. Adopting a Culture of Collaboration and Communication
Major Features:
- Breaking Down Silos:
- DevOps thrives on breaking down traditional silos between development, operations, and other IT teams. This strategy fosters collaboration and ensures that all teams work toward common goals, improving communication and efficiency.
- Cross-functional teams are encouraged, where developers, operations personnel, and business stakeholders collaborate throughout the software development lifecycle (SDLC).
- Shared Ownership:
- A key part of this strategy is ensuring shared ownership of the application, infrastructure, and services. Both developers and operations teams share the responsibility of maintaining the service, ensuring that everyone is invested in its success.
- Increased Transparency:
- Open communication and transparency across teams help ensure that there are no hidden bottlenecks or issues. Regular stand-ups, collaborative tools (like Slack or Microsoft Teams), and shared dashboards encourage transparency and quick problem resolution.
- Fostering Trust:
- Trust between development and operations is essential for a successful DevOps implementation. Encouraging knowledge-sharing, respecting team expertise, and prioritizing empathy over competition builds trust among teams.
2. Automation of Key Processes
Major Features:
- Automating Repetitive Tasks:
- One of the core principles of DevOps is automation. Automation tools can significantly reduce the manual effort involved in tasks such as testing, code integration, deployment, and infrastructure provisioning.
- Common tools for automation include Jenkins for CI/CD pipelines, Ansible and Chef for configuration management, and Terraform for infrastructure provisioning.
- Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery (CI/CD):
- The CI/CD pipeline is a foundational part of DevOps, enabling teams to automatically integrate code changes and deploy applications without manual intervention.
- By automating these pipelines, organizations can ensure that new code is tested, built, and deployed faster and more reliably, reducing the time between development and production.
- Automated Testing:
- Automated testing tools like JUnit, Selenium, and Postman help ensure that code changes do not break existing functionality, thereby improving code quality and reliability.
- By automating testing, teams can detect issues early and address them before they reach production, preventing bugs and performance issues from affecting the end-users.
- Infrastructure as Code (IaC):
- Automating infrastructure management using IaC tools like Terraform and CloudFormation ensures consistent environments, reduces human error, and speeds up the process of provisioning and managing infrastructure.
3. Continuous Monitoring and Feedback
Major Features:
- Real-Time System Monitoring:
- Continuous monitoring ensures that teams can observe the health of their applications and infrastructure in real-time. Tools like Prometheus, Grafana, and Nagios provide visibility into performance, user interactions, and resource utilization.
- Proactive monitoring helps identify and resolve issues quickly, reducing downtime and improving system stability.
- Feedback Loops:
- Regular feedback is essential for continuous improvement in DevOps. After each deployment, performance data and user feedback are collected, allowing teams to assess the impact of their changes.
- Feedback loops are established at all stages of the SDLC to ensure that the product meets user expectations and business goals. This can be achieved through customer feedback, system performance data, and internal reviews.
- Incident Management:
- Automated alerts and ticketing systems (such as PagerDuty or Opsgenie) notify teams about system failures, performance degradation, or security breaches, ensuring rapid response to incidents.
- The ability to monitor and respond to issues in real time leads to faster recovery times and improved service reliability.
- Root Cause Analysis:
- With continuous monitoring, teams can conduct post-mortems and root cause analysis (RCA) after incidents to understand the underlying causes. This helps prevent similar issues from recurring and improves the overall development process.
4. Security Integration (DevSecOps)
Major Features:
- Incorporating Security Early in the SDLC:
- DevSecOps is the practice of integrating security into the DevOps pipeline, rather than treating it as an afterthought. This proactive approach ensures that security vulnerabilities are identified and addressed early in the development lifecycle.
- Security tools like OWASP ZAP, Snyk, and Fortify can be integrated into the CI/CD pipeline to automatically detect vulnerabilities and ensure compliance.
- Automated Security Testing:
- Just as testing is automated in DevOps, security testing should be automated to scan code and infrastructure for vulnerabilities. This includes static analysis, dependency checks, and penetration testing.
- Automating security checks ensures that vulnerabilities are caught early, reducing the likelihood of breaches in production.
- Continuous Compliance:
- DevOps teams can implement continuous compliance by automating checks for regulatory standards and security policies. Tools like Chef InSpec and Puppet help automate compliance checks, ensuring that infrastructure and applications meet required standards.
- Continuous compliance reduces the risk of regulatory violations and ensures that security policies are enforced consistently across all stages.
- Secure Infrastructure Management:
- By automating infrastructure provisioning with IaC tools and using encryption at rest and in transit, DevSecOps ensures that the infrastructure is secure and resilient to attacks.
- This approach minimizes human error and ensures that secure configurations are deployed consistently across all environments.
5. Cultural and Organizational Transformation
Major Features:
- Shifting from a Traditional to a Collaborative Culture:
- DevOps requires a cultural shift in how teams collaborate. Development, operations, and security teams must work together as part of a single unified team, rather than operating in isolated silos.
- Encouraging cross-functional teams, where members contribute to various stages of the SDLC, fosters better communication and more efficient problem-solving.
- Encouraging Continuous Learning and Improvement:
- DevOps emphasizes a culture of continuous learning, where teams are encouraged to experiment, innovate, and improve their skills. This mindset helps keep teams engaged and leads to higher quality products.
- Providing regular training, retrospectives, and encouraging feedback from all levels of the organization helps drive continuous improvement.
- Leadership Support and Investment:
- Successful DevOps adoption requires strong leadership support. Leadership should not only endorse DevOps practices but also actively invest in the necessary tools, training, and resources.
- By fostering an environment that supports experimentation, learning, and change, organizations can better navigate the challenges of DevOps implementation.
- Shared Metrics and KPIs:
- DevOps emphasizes using shared metrics and KPIs across teams to measure success. These metrics may include deployment frequency, change failure rate, lead time, and mean time to recovery (MTTR).
- Tracking these metrics ensures that all teams are aligned toward common goals and continuously strive for improvement.
6. Continuous Improvement and Feedback Loops
Major Features:
- Iterative Development and Feedback:
- DevOps is all about continuous improvement, and one of the best ways to achieve this is through iterative development. By making small, incremental changes and obtaining constant feedback, teams can continuously refine and improve their product.
- Agile methodologies, often combined with DevOps, ensure that releases are tested and refined regularly, reducing the time it takes to address user feedback and performance data.
- Post-Deployment Review:
- After every release, teams conduct post-deployment reviews and retrospectives to identify areas for improvement. These reviews allow teams to discuss what went well and what could be done better in the future.
- Continuous feedback from these reviews helps optimize the DevOps pipeline, improve collaboration, and streamline workflows.
- Proactive Problem Solving:
- Instead of merely reacting to issues, DevOps teams are encouraged to anticipate potential problems and solve them before they arise. This proactive approach minimizes downtime and maximizes service availability.
- Tools like JIRA and Trello are often used to track and address issues as part of the continuous improvement process.
Choosing the Right DevOps Implementation Strategy
Choosing the right DevOps implementation strategy is critical to achieving the goals of faster software delivery, improved collaboration, and higher quality. By adopting the appropriate DevOps practices—such as fostering collaboration, automating workflows, integrating security, and continuously monitoring performance—organizations can optimize their software development and operations processes.
DevOps is an ongoing journey of transformation, requiring cultural shifts, the adoption of new tools, and a focus on continuous improvement. By aligning teams, processes, and tools, organizations can achieve the agility and scalability needed to stay competitive in today’s fast-paced technological landscape.

 Starting: 1st of Every Month
Starting: 1st of Every Month  +91 8409492687 |
+91 8409492687 |  Contact@DevOpsSchool.com
Contact@DevOpsSchool.com