Upgrade & Secure Your Future with DevOps, SRE, DevSecOps, MLOps!
We spend hours on Instagram and YouTube and waste money on coffee and fast food, but won’t spend 30 minutes a day learning skills to boost our careers.
Master in DevOps, SRE, DevSecOps & MLOps!
Learn from Guru Rajesh Kumar and double your salary in just one year.
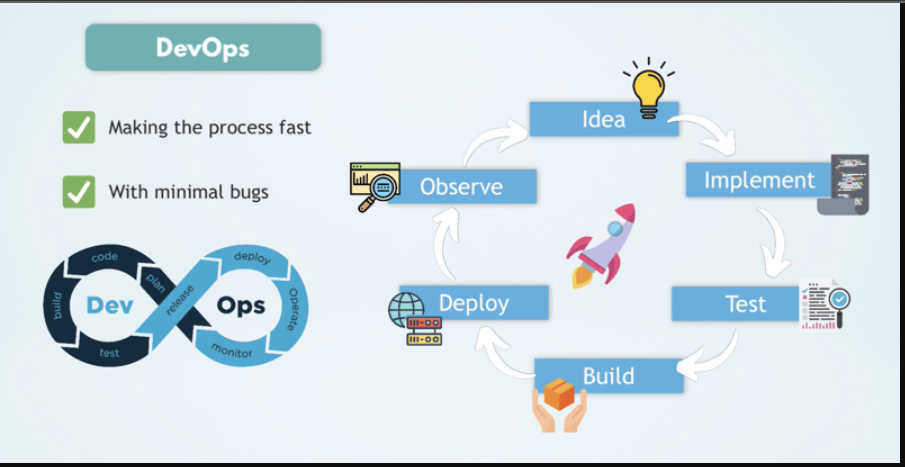
DevOps is a combination of development (Dev) and operations (Ops) practices that aims to improve the efficiency, collaboration, and quality of software delivery. It is a cultural shift that focuses on breaking down silos between traditionally separate teams to improve the speed, reliability, and quality of software deployment. By integrating automation, monitoring, and collaboration, DevOps helps organizations deliver software faster, with fewer errors, and better alignment with customer needs.
In this post, we will explore the meaning of DevOps, its core components, and how it’s implemented in modern software development environments.
1. DevOps as a Cultural Movement
Major Features:
- Collaboration Across Teams:
- DevOps is not just a set of tools or technologies but a cultural shift that encourages collaboration between development and operations teams. These teams traditionally worked in silos, but DevOps emphasizes the importance of shared responsibilities in building, testing, and deploying software.
- Shared Goals:
- With DevOps, both developers and operations professionals work toward common goals, such as delivering high-quality software quickly and improving operational efficiency. This alignment reduces friction, minimizes misunderstandings, and speeds up software delivery.
- Fostering Communication:
- Regular communication, collaboration, and feedback between teams are central to DevOps. Daily stand-ups, collaborative workflows, and integrated systems encourage everyone to stay on the same page and improve workflows continuously.
- Focus on Continuous Improvement:
- DevOps encourages an attitude of continuous improvement, where teams iteratively improve their processes, tools, and products based on feedback from customers, end-users, and the system itself.

2. DevOps and Automation
Major Features:
- Automated CI/CD Pipelines:
- At the heart of DevOps is automation. Continuous Integration (CI) and Continuous Delivery (CD) pipelines help automate the process of code integration, testing, and deployment. This ensures that new code is tested and deployed quickly and reliably.
- Infrastructure as Code (IaC):
- DevOps leverages Infrastructure as Code (IaC), where infrastructure is provisioned and managed using code rather than manual processes. Tools like Terraform, AWS CloudFormation, and Ansible allow teams to automate and version control their infrastructure just like they do with software code.
- Automated Testing:
- In DevOps, automated testing is critical to ensure that software is error-free before it’s deployed to production. Tools like Selenium, JUnit, and JUnit5 are used to automate unit tests, integration tests, and functional tests to catch bugs early in the development process.
- Error-Free Deployments:
- By automating the build and deployment process, DevOps reduces human error and ensures that deployments are consistent and repeatable across environments (development, staging, production).
3. DevOps and Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD)
Major Features:
- CI/CD Pipeline:
- Continuous Integration (CI) is the practice of automatically integrating code changes into a shared repository and testing them to identify issues early. Continuous Deployment (CD) ensures that code is automatically pushed to production once it has passed all tests, making software delivery seamless and faster.
- Quick Feedback Loop:
- CI/CD enables a quick feedback loop, allowing developers to fix issues in real-time. With immediate feedback from automated testing, developers can address bugs quickly and reduce delays in the software release cycle.
- Faster Releases:
- DevOps practices with CI/CD pipelines enable businesses to release software updates frequently and reliably, which is essential for maintaining competitive advantage in fast-paced markets.
- Efficiency and Agility:
- By automating integration and deployment, DevOps makes the software development cycle more efficient and agile, allowing teams to adapt quickly to changing requirements and priorities.
4. DevOps and Monitoring
Major Features:
- Real-Time Monitoring:
- DevOps includes continuous monitoring of both infrastructure and applications to ensure they perform as expected. Tools like Prometheus, Grafana, and Datadog are used to track system health and identify performance issues in real-time.
- Proactive Issue Resolution:
- Continuous monitoring helps teams detect issues early and take proactive measures to resolve them. This minimizes system downtime and improves the user experience.
- Visibility and Insights:
- Monitoring provides real-time visibility into software performance and user interactions, which helps teams identify areas for improvement. By analyzing logs, performance metrics, and system alerts, teams can better understand and optimize their applications.
- Automated Scaling:
- Based on the data collected through monitoring, DevOps allows for automatic scaling of infrastructure resources to meet increasing demand. This helps ensure applications remain responsive and reliable during traffic spikes.
5. DevOps and Security (DevSecOps)
Major Features:
- Security Integration:
- DevOps isn’t just about speed and efficiency; it also integrates security into the development lifecycle, a practice known as DevSecOps. Security tests and protocols are embedded throughout the CI/CD pipeline to identify vulnerabilities early in the development process.
- Automation of Security Tasks:
- DevSecOps tools like Snyk and Aqua Security automate the process of scanning code for security issues, ensuring that vulnerabilities are detected and addressed before deployment.
- Compliance and Governance:
- DevOps practices help maintain compliance with industry regulations by enforcing security policies and audit trails. This ensures that sensitive data and systems are protected from external and internal threats.
- Shifting Left:
- The idea of shifting security left means incorporating security practices early in the development process, rather than waiting until later stages, helping to identify and mitigate security risks before they become larger problems.
6. DevOps and Cloud Computing
Major Features:
- Cloud-Native DevOps:
- Cloud platforms like AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud provide the infrastructure and tools needed to implement DevOps practices in the cloud. With cloud-native applications, DevOps allows for rapid provisioning, scaling, and deployment of resources.
- Elasticity and Scalability:
- Cloud computing provides the flexibility to scale infrastructure dynamically based on real-time demand, which is an essential feature for modern DevOps. This ensures applications remain resilient even during peak usage times.
- Containerization and Orchestration:
- DevOps makes heavy use of containers (e.g., Docker) and container orchestration tools (e.g., Kubernetes) to ensure applications are consistent and portable across different environments, whether on-premise or in the cloud.
- Cost Optimization:
- Cloud-based DevOps practices help optimize resource usage, ensuring that organizations only pay for the resources they use, which reduces costs and improves operational efficiency.
The Meaning and Impact of DevOps
DevOps represents a major shift in how software development and IT operations work together to deliver high-quality software quickly and reliably. By embracing automation, collaboration, continuous integration/deployment, monitoring, and security, DevOps enables businesses to respond faster to customer needs, improve operational efficiency, and ensure better-quality software.
At its core, DevOps is about a culture of collaboration and continuous improvement. It requires investment in the right tools, processes, and organizational changes, but the result is a more agile, secure, and resilient software development lifecycle. Whether you’re a developer, IT operations specialist, or business leader, understanding what DevOps means and its core practices will help you align your organization with modern best practices and stay competitive in a rapidly evolving market.

 Starting: 1st of Every Month
Starting: 1st of Every Month  +91 8409492687 |
+91 8409492687 |  Contact@DevOpsSchool.com
Contact@DevOpsSchool.com