Upgrade & Secure Your Future with DevOps, SRE, DevSecOps, MLOps!
We spend hours on Instagram and YouTube and waste money on coffee and fast food, but won’t spend 30 minutes a day learning skills to boost our careers.
Master in DevOps, SRE, DevSecOps & MLOps!
Learn from Guru Rajesh Kumar and double your salary in just one year.
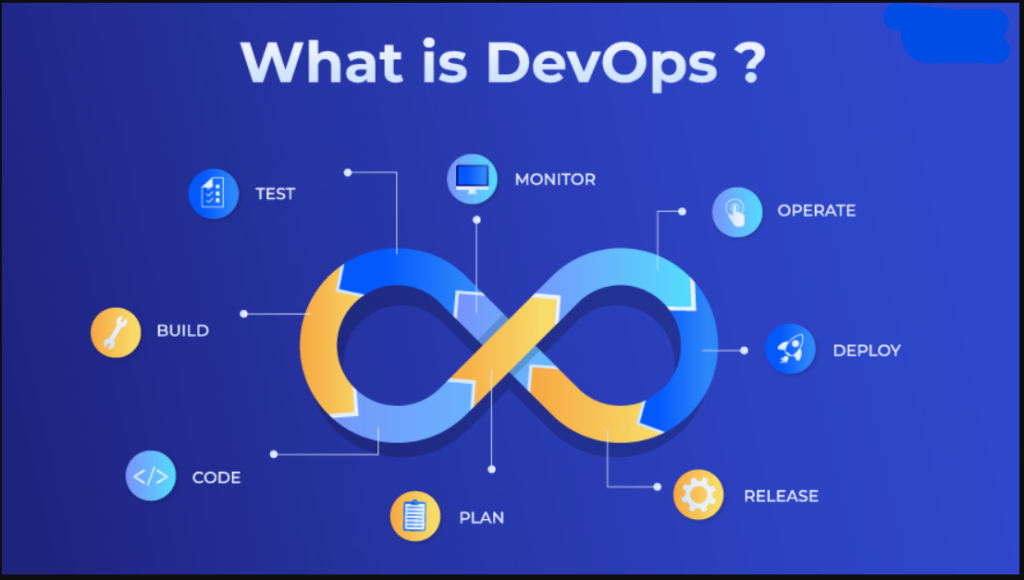
DevOps is a set of practices, tools, and cultural philosophies that aim to increase the collaboration between software development (Dev) and IT operations (Ops) teams. By unifying these traditionally separate groups, DevOps seeks to shorten the development lifecycle, enhance the quality of software, and ensure faster and more reliable releases. The core philosophy of DevOps revolves around automation, continuous integration, continuous deployment, and a culture of shared responsibility.
In this post, we will dive into what DevOps is, its essential features, and how its implementation leads to more efficient and collaborative software delivery processes.
1. DevOps as a Cultural Shift
Major Features:
- Collaboration Between Development and Operations:
- DevOps promotes a culture of collaboration and communication between development and operations teams, breaking down silos and encouraging them to work toward a common goal: delivering high-quality software quickly and efficiently.
- Shared Responsibilities:
- In a DevOps environment, developers and operations teams share the responsibility for the entire software lifecycle, from coding and testing to deployment and monitoring. This leads to greater accountability and better overall results.
- Continuous Feedback:
- Regular feedback loops between teams are essential to DevOps. By continuously sharing insights and monitoring progress, teams can quickly identify issues, resolve them, and improve processes.
- Cultural Transformation:
- Adopting DevOps means embracing a cultural transformation within organizations. It encourages transparency, fosters innovation, and supports the agile development process.
2. Automation in DevOps
Major Features:
- Automating Repetitive Tasks:
- One of the primary objectives of DevOps is to automate repetitive tasks in the software development and deployment lifecycle. This includes tasks like code integration, testing, deployment, and infrastructure management, all of which are automated to reduce manual intervention and human error.
- CI/CD Pipelines:
- Continuous Integration (CI) and Continuous Delivery (CD) are foundational practices in DevOps. CI/CD pipelines automate the process of integrating, testing, and deploying code, enabling teams to release software more frequently and with higher confidence.
- Infrastructure Automation:
- With Infrastructure as Code (IaC) tools like Terraform and CloudFormation, DevOps enables the automatic provisioning and management of infrastructure. This eliminates manual configuration and ensures that environments are consistent and reproducible.
- Scalability and Efficiency:
- Automation allows DevOps teams to handle complex systems with ease and efficiency, ensuring that software can scale quickly and efficiently in response to changing business needs.
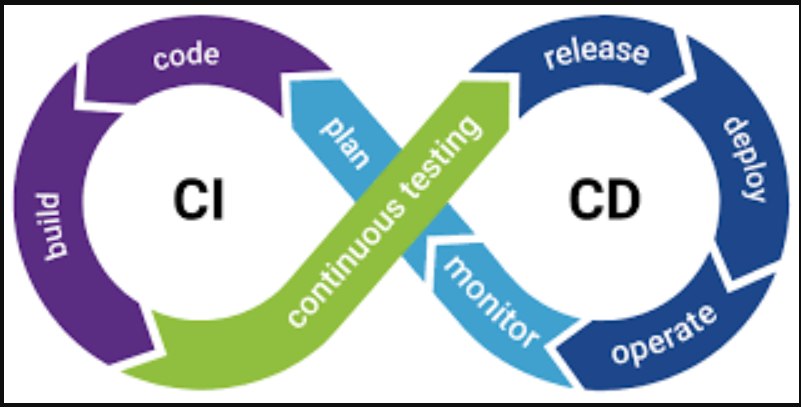
3. Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD)
Major Features:
- Continuous Integration:
- CI is the practice of frequently integrating code into a shared repository. Every integration is automatically tested to detect issues early in the development cycle. This helps developers catch bugs faster and improves code quality.
- Continuous Delivery:
- CD takes CI one step further by automating the process of delivering the integrated code to production environments. This allows software to be released continuously without manual intervention, leading to faster time-to-market and reduced risks.
- Faster Feedback Loop:
- CI/CD pipelines ensure that feedback is provided instantly. Developers can see the results of their changes immediately, enabling them to address issues quickly and maintain a steady pace of development.
- High-Quality Software:
- With automated testing and deployment processes, DevOps ensures that the software being released is high quality and reliable, reducing the likelihood of bugs or issues in production.
4. Monitoring and Continuous Improvement
Major Features:
- Real-Time Monitoring:
- DevOps places a strong emphasis on real-time monitoring of both applications and infrastructure. This ensures that teams can track performance, detect issues, and optimize the system before it affects end users.
- Proactive Issue Resolution:
- With constant monitoring, DevOps teams can detect problems proactively and take corrective action. This minimizes downtime, enhances user experience, and maintains the reliability of the system.
- Feedback Loops for Improvement:
- DevOps emphasizes continuous improvement. By collecting feedback from both development and operations teams, DevOps fosters a culture of iteration and optimization. This ensures that processes and systems evolve based on real-time data and experiences.
- Tools for Monitoring:
- Tools like Prometheus, Grafana, Datadog, and New Relic provide essential monitoring capabilities, offering insights into the health of applications and infrastructure, and identifying bottlenecks or failure points in real time.
5. Security in DevOps (DevSecOps)
Major Features:
- Security Integration:
- In traditional IT models, security is often seen as a separate function handled at the end of the software development process. In DevOps, security is integrated throughout the pipeline in what is known as DevSecOps. Security is no longer an afterthought but is embedded at every stage of development.
- Automated Security Testing:
- DevOps tools automate security testing at every stage of the development lifecycle. This includes scanning code for vulnerabilities, ensuring compliance with security standards, and automating security patching for applications and systems.
- Security Monitoring:
- Continuous monitoring in DevOps is not limited to system performance. It also includes security monitoring to detect any potential breaches, unauthorized access, or vulnerabilities in real time.
- Shift-Left Security:
- Shift-left security means incorporating security practices earlier in the development process, rather than waiting until the deployment phase. This reduces the risk of security issues and improves overall software safety.
6. DevOps Tools and Technologies
Major Features:
- Automation and Configuration Management:
- A variety of tools enable the automation and management of DevOps processes. Popular tools like Jenkins, GitLab, Ansible, Docker, and Kubernetes help automate key tasks like code integration, testing, deployment, and containerization.
- Version Control Systems:
- Git is widely used in DevOps for version control. By managing code changes and maintaining multiple versions of the software, version control ensures that teams can collaborate efficiently and track changes across all stages of development.
- Collaboration and Communication Tools:
- Effective communication and collaboration are essential for DevOps success. Tools like Slack, Jira, and Trello facilitate seamless communication among cross-functional teams and improve workflow management.
- Cloud and Infrastructure Tools:
- Cloud platforms like AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud are essential for DevOps teams to manage resources and deploy applications in a scalable and cost-effective manner. Tools like Terraform and CloudFormation help automate infrastructure provisioning in the cloud.
The Power and Impact of DevOps
DevOps is much more than just a set of practices or tools. It is a cultural shift that transforms the way teams collaborate, innovate, and deliver software. By integrating development and operations teams, automating processes, and emphasizing continuous monitoring and feedback, DevOps enables organizations to deliver high-quality software faster and more efficiently.
Whether you’re a software developer, an IT operations specialist, or a business leader, adopting DevOps practices can lead to improved productivity, better customer satisfaction, and a more agile software development lifecycle. Embracing DevOps means embracing collaboration, automation, monitoring, and continuous improvement, all of which drive long-term success in today’s fast-paced, technology-driven world.

 Starting: 1st of Every Month
Starting: 1st of Every Month  +91 8409492687 |
+91 8409492687 |  Contact@DevOpsSchool.com
Contact@DevOpsSchool.com